Ahrefs has a plethora of useful tools and resources. Since the publishing of that post, a few new features have been added. One of these features in the “Internal Backlinks” tab:

What Does it Do?
Put simply, it shows which pages link to which pages, all within your website. Internal linking is important for site organization, user experience, and crawling ease. The Internal Backlinks tool helps you to understand your linking structure, which pages could use more links, and which pages are only ranking well because of their internal linking.
Before going into the functions, let’s go into the options.
Setting Up a Search

Group Similar/All
The first option to toggle is whether to look at all backlinks or just the unique ones. When All is selected, it will show you all of the links of every page, including the ones that are on every page. That means it will show the link to your contact page that appears in the upper-right hand corner of the page throughout the website. This doesn’t help if you’re trying to see if you need to link to your contact page more in your blogs. When Group Similar is selected, it filters the links that appear on every page with the exact same anchor text out of the listings.
Link Type
There’s a pretty wide range of link types to look at. Some of the more important ones to know about are Dofollow and Nofollow.
- Dofollow – These are links that search engines are allowed to follow when crawling a site. Dofollow links add authority with both internal and external links.
- Nofollow – Nofollow links do not let search engines follow them while crawling. These should largely be the links you don’t need crawlers to crawl on every single page. This means the links in the navigation bar and the footer are generally safe to be nofollow. It is also a good link type to check to make sure links that can be dofollow are attributed as such.
Platform
What’s available to toggle in this section depends on how your website is set up, but chances are you have the options of “All” and “Blogs.” As you’ve probably guessed, it means you can filter what types of pages you’re seeing.
Language
As with Platform, the languages you can check up on are just the languages that your site has. If you have a multilingual setup then you can see which pages are being linked to in all relevant languages.
Traffic
In Ahrefs’ own words, traffic “estimates the total monthly search traffic to the referring page from the top 100 organic search results. It is…the sum of traffic from all organic keywords.” This metric is manageable by listing your lower and upper limits for which pages you want to see, with higher numbers being better. You can use this to see which pages are getting low traffic and trying to improve them.
Search Bar
The search bar is useful when looking at specific keywords and/or pages. It allows you to either include or exclude, with include being the default. This means that if you have one page that performs so well it’s an outlier, you can exclude it.
Targets
The final section in the search box is what you’re targeting. You can decide to focus on URLs, titles, anchor text, and/or surrounding text, depending on your needs.
Examining Functions
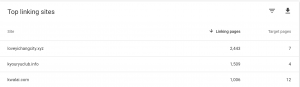
Now let’s get into the functionality. As for link structures and seeing where you can build out, there are some pages where it makes sense that it’s easily accessible from just about every page on the website. An example of such a page would be your contact page.
If I wanted to find how many blog posts linked to the contact page, I might set up my search like this:
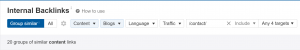
This will show me all of the blogs that link to the contact page and the value of those pages. Since there are only 20 blog posts that fit the description, there’s probably room to add a few more, especially to higher-performing posts.
If you want to know if any of your higher-performing pages owe their rank to internal linking, or if you want to improve the ranking of some of your lower performing pages, you can find those in Internal Backlinks as well.
Measuring Authority
To do this, sort all the pages in the Internal backlinks section by UR (URL rating, a metric calculated by Ahrefs). When you have found a page with a high UR, search for it in the search bar, narrowing the search to only include URLs of referring pages. This will show all the pages that it already links to. If you think you can add more links with making the page oversaturated, add more.
On the flip side, if you’re wondering what pages could be improved by being linked to, sort by lowest to highest UR. Once you find a page that you think could use some more traffic, search for that page or keywords relating to that page. You will find which pages are linking to it, and which pages cover the topics discussed on the page that could serve as anchor text.
Utilizing These Tools
There’s obviously more you can do with Ahrefs and with this tool in particular. Understanding your links and ratings is an important step to understanding your website. To learn about how Ahrefs can help your law firm, contact Mockingbird.