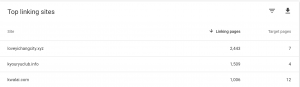
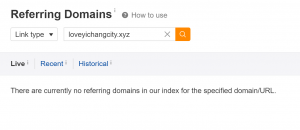
Google tries to be vigilant about spam. It really does. Link building schemes, black hat tactics, and malicious software are some of the main things Google looks for. When it finds them, it might respond with a Manual Action.
So What is a Manual Action?
A manual action is when an actual, real-life member of Google’s team checks in on your websites and penalizes it for going against best practices. Manual actions can take a variety of forms and can be consequences of a variety of things.
Types of Manual Actions
-
Partial Matches (partial de-indexing)
If Google finds pages in violation of best practices it might de-index those specific URLs. This means that they will no longer show up in search results. This can be done to a page, sub-domain, forum, or any section of a domain. A partial match action is generally the best possible scenario for webmasters who are facing spam attacks, as the domain is still functioning and traffic can still find your site. It is still important to try and fix the issue and lift the action as soon as possible.
-
Whole Site Matches (total de-index)
If the problem is found to be larger than a few key URLs, Google may de-index the entire domain. This is a harsh penalty, but it can be reversed once the site complies with webmaster guidelines. Whole site matches are generally implemented when a site flagrantly ignores guidelines by cloaking content, redirecting users, and exposing users to malicious content. If your site is facing a whole site match, you need to consider what brought you there and if you need to change course.
What Might Cause a Manual Action
Google has a long list of reasons for invoking manual actions. Most of them involve spam links, as link building schemes are about the most forms of breaking best practices that webmasters do. The complete list includes:
-
User-generated spam
User-generated spam is spam that comes not from the webmaster, but the users of the website. This happens in forums and comments sections of websites.
-
Unnatural links to and from your site
This refers to link building schemes and spam attacks. If your site is suddenly sending thousands of links to a single, low authority site or is showing signs of spammy link exchanges, or has thousands of links from one low-authority site, Google might reprimand the URL or domain.
-
Thin or duplicate content
This is more subjective, as some sites do not need large amounts of content. That being said, many sites have unnecessary numbers of pages with practically duplicate content, which often sees penalties.
-
Cloaked content/images
This is a pretty old-school black hat technique, and Google is pretty good at finding when people try to implement it. Cloaking refers to showing different content to humans than to the GoogleBot. They can do this by having one image cover another, writing paragraphs of keywords in the same color as the background of the page, or stuffing keywords into gibberish text. Google really doesn’t appreciate these techniques and comes down pretty hard on those that do it.
-
Redirects
Redirects, whether desktop or mobile, refers to when a user clicks on a link to one website then gets redirected to another, completely unrelated, URL. The penalties are usually applied when the redirect goes to a site that is harmful or the redirect is malicious in it’s intent (i.e. sending a user looking for cartoons to a porn site).
How to Fix a Manual Action
Fixing a manual action starts by fixing the problem you were originally penalized for. If you were hit for displaying spam comments you might want to delete those comments and block the IPs they were sent from. If you were hit with a spam link attack, go through the disavow process and clean up your referrals. Google has recommendations on how to fix your website after all types of manual actions.
Once you have made the changes you need to make, you can make a reconsideration request. This is a request for Google to re-review your website and lift the manual action.
Sometimes you do the work, write the request, and get a denial. This means you didn’t do the fullest work you needed to do. Get back to work and draft a new reconsideration request.
Final Thoughts
Don’t mess with Google. Even if they wrongly put a manual action against you, you apologize and follow the recommendations they give you. Google holds all the power.